Cochlear implants & Hearing Aid

Audiometry
Audiometry or Pure tone audiometry (PTA) test measures a person’s ability to hear different sounds, across different pitches, or frequencies. A qualified audiologist can perform the test.
Audiometry tests can detect
- 1. sensorineural hearing loss – damage to the nerve or cochlea or
- 2. conductive hearing loss – damage to the eardrum or the tiny ossicles (bones).
Audiometry tests can be performed on children (who can respond consistently to pure tone) and even on adults. The children who can not respond to tests are assessed by an electrophysiological test like BERA and OAE.
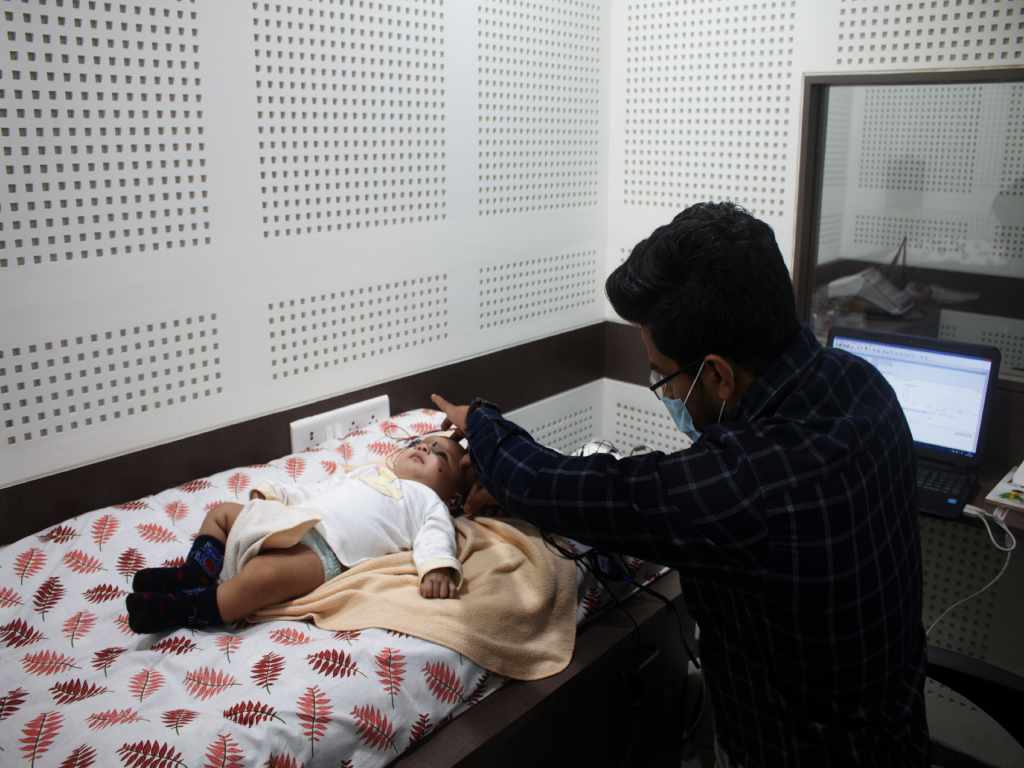
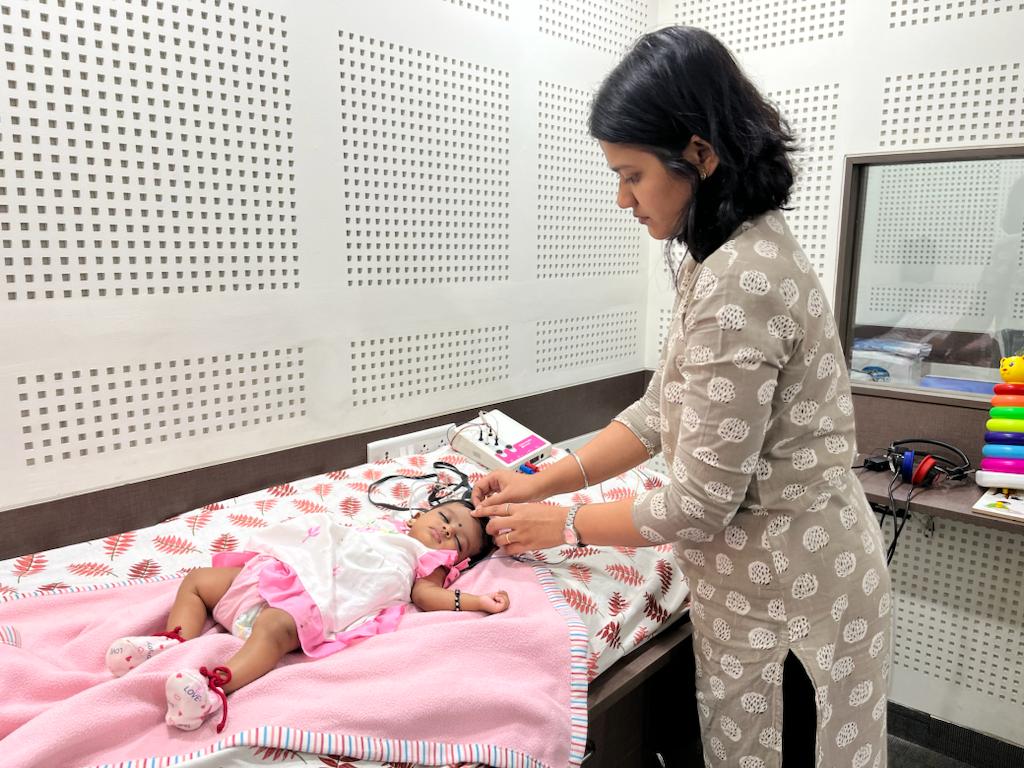

BERA and OAE
Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA) is an electrophysiological test to estimate the hearing capacity of the child. This test is carried out in a state of natural sleep or under sedation. The response of the eighth nerve and the brainstem to sound is picked up by the electrodes. This information is depicted as waveforms by the software to know the hearing acuity of the child. It is a reliable way of estimating the hearing threshold when behavioural responses are inconsistent.
Otoacoustic emissions (OAE) is a physiological test that is used in screening for hearing loss in infants and children. It measures the activity of the outer hair cells in the cochlea (inner ear). Functional outer hair cells give a pass result and any dysfunction in the outer hair cell shows a refer result. A child with refer report is further recommended for complete diagnostic evaluation to know the hearing threshold.
OAE and BERA tests can be done on babies as young as 1 day old.
Hearing loss is classified on the basis of audiogram as follows:
- 1. Normal = -10 to 15 dB Hl
- 2. Minimal= 16 to 25 dB Hl
- 3. Mild = 26 to 40 dB Hl
- 4. Normal = -10 to 15 dB Hl
- 5. Normal = -10 to 15 dB Hl
Hearing aids and cochlear implant
Hearing aids can be analogue basic amplification devices or digitally programmable devices which help an individual with hearing loss to hear better. Digital hearing aids are preferable as they amplify the speech sounds and reduce the background noise which gives better clarity of speech. It can be adjusted by an audiologist to give the appropriate amount of amplification, to avoid any discomfort.
Types of Hearing Aid:
- 1. Body-level hearing aid
- 2. Behind the ear (BTE)
- 3. Receiver in the canal (RIC)
- 4. Completely in the canal (CIC)
- 5. Invisible in the canal (IIC)
A cochlear implant is a small, complex electronic device that can help to provide a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing. Cochlear implants bypass damaged portions of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve. Signals generated by the implant are sent by way of the auditory nerve to the brain, which recognizes the signals as sound.
The implant consists of an
- 1. External portion: processor (sits behind the ear)
- 2. Internal portion: implant (surgically placed under the skin).
Auditory Verbal Therapy
(AVT) is a highly specialised, family centred, early intervention program. It is
put into action immediately after a child is given access to the world of sounds,
either through hearing aids, or cochlear implants.
Although these hearing devices enable all sounds to reach the brain, listening and making sense of the sounds is a skill which needs to be taught. This is addressed in AVT.
Parents and caregivers play a primary role in this specialised therapy, where the therapy equips them with the tools and skills required to develop their child’s listening and spoken language. Different strategies are used to maximize the child’s auditory attention and to develop a listening attitude.
Ultimately, AVT aims to timulate and develop the auditory areas of the brain, which subsequently helps in the development of language.
Government Aid
Acts/ Laws/ Concessions for Special Children
Ministry of social justice and empowerment, Govt. of India
Disability Act :
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016 was enacted on 28.12.2016 which came into force from 19.04.2017.
Click here for further details:https://legislative.gov.in/sites/default/files/A2016-49_1.pdf
National Handicapped Finance and Development Corporation
National Handicapped Finance and Development Corporation (NHFDC) is a Central Public Sector Undertaking under the aegis of Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, Government of India. The Corporation is registered under section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (Corresponding provisions of section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013) on 24.01.1997 as a company not for profit.
Click here for further details
http://www.nhfdc.nic.in/default.aspx
Schemes under the Government of Maharashtra
The Department of Social Justice and Special Assistance Department of Government of Maharashtra have several schemes for the hearing impaired under Disability Welfare.
Click here to for further details:
https://sjsa.maharashtra.gov.in/en/scheme-category/disability-welfare
Schemes under Central Government of India
ADIP Scheme for Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implants
The ADIP Scheme is in operation since 1981 with the main objective to assist the needy disabled persons in procuring durable, sophisticated and scientifically manufactured, modern, standard aids and appliances that can promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation by reducing the effects of disabilities and enhance their economic potential.
Click here for further details:
The speech and language training provided to hearing-impaired babies is a comprehensive
process that typically spans a period of 3-4 years.

